ks test r package|kolmogorov smirnov test example : mfg Function to perform two sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test on rows/columns of matrices. Main arguments and results were intentionally matched to the ks.test() function from default stats .
webWatch the second installment of the Hunger Games series, where Katniss and Peeta face a new threat from the Capitol. This title may not be available from your location in Brazil.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Novoline Utility Mod site. © 2020, Novoline Client. Icons are provided by Flaticon
Details. If y is numeric, a two-sample test of the null hypothesis that x and y were drawn from the same continuous distribution is performed. Alternatively, y can be a character string naming a .
The two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test is a non-parametric method used to compare the empirical cumulative distribution functions (ECDFs) of two independent samples to determine if they are drawn from the same underlying .
Description. Performs one or two sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests. Usage. ks.test(x, y, ., alternative = c("two.sided", "less", "greater"), exact = NULL, tol=1e-8, .ks.test(x, y, ., alternative = c("two.sided", "less", "greater"), exact = NULL) Arguments. Details. If y is numeric, a two-sample test of the null hypothesis that x and y were drawn from the same .The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test in R can be performed with the ks.test() function from the base "stats" package. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test is a non-parametric test that can be used to .
Function to perform two sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test on rows/columns of matrices. Main arguments and results were intentionally matched to the ks.test() function from default stats .Description. Perform a one- or two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Usage. ks.test(x, .) ## Default S3 method: ks.test(x, y, ., alternative = c("two.sided", "less", "greater"), exact = NULL, .Performs the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for comparing the distribution of a sample to a specified distribution. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test is a type of non-parametric test of the equality of discontinuous and continuous a 1D probability distribution that is used to compare the sample with the reference probability test (known as one .
ks two sample test
Details. If y is numeric, a two-sample test of the null hypothesis that x and y were drawn from the same continuous distribution is performed.. Alternatively, y can be a character string naming a continuous (cumulative) distribution function (or such a function), or an ecdf function (or object of class stepfun) giving a discrete distribution.In these cases, a one-sample test is carried out of .Performs the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for comparing the distribution of a sample to a specified distribution. 0. Skip to Content Home Resources R Tutorials R Functions External R Resources Foundational Statistics Products Mental Health Screener Free R Apps .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
ks test for uniform distribution
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test in R can be performed with the ks.test() function from the base "stats" package. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test is a non-parametric test that can be used to test whether a sample fits a distribution , or if two samples are from the same distribution. Details. If y is numeric, a two-sample test of the null hypothesis that x and y were drawn from the same continuous distribution is performed.. Alternatively, y can be a character string naming a continuous (cumulative) distribution function (or such a function), or an ecdf function (or object of class stepfun) giving a discrete distribution.In these cases, a one-sample .
The version of ks.test() in the dgof R package (article, cran) adds some capabilities not present in the default version of ks.test() in the stats package. Among other things, dgof::ks.test includes this parameter: simulate.p.value: a logical indicating whether to compute p-values by Monte Carlo simulation, for discrete goodness-of-fit tests only.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
R/ks.test.R defines the following functions: Any scripts or data that you put into this service are public.Details. If y is numeric, a two-sample test of the null hypothesis that x and y were drawn from the same continuous distribution is performed.. Alternatively, y can be a character string naming a continuous (cumulative) distribution function, or such a function. In this case, a one-sample test is carried out of the null that the distribution function which generated x is distribution y with .Illustration of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistic. The red line is a model CDF, the blue line is an empirical CDF, and the black arrow is the KS statistic.. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (K–S test or KS test) is a nonparametric test of the equality of continuous (or discontinuous, see Section 2.2), one-dimensional probability distributions that can be used to test whether a sample came from .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. The usual Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for two vectors X and Y, of size m and n rely on the empirical cdfs E_x and E_y and the test statistic D = sup_{t\in (X, Y)} |E_x(x) - E_y(x)). This modified Kolmogorov-Smirnov test relies on two modifications. . R Package Documentation. rdrr.io home R language documentation Run R code online. Browse R . Performs two-sample nonparametric multivariate test of means based on the minimum spanning tree (MST) and Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic. It tests the null hypothesis that a set of features has the same mean in two conditions versus different means.
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.I tried to use the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to test normality of a sample. This is a small simple example of what I do: x <- rnorm(1e5, 1, 2) ks.test(x, "pnorm") Here is the result R gives me: One-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test data: x D = 0.3427, p .Perform a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for one sample or two samples using kernel method. RDocumentation. Learn R. Search all packages and functions. snpar (version 1.0) Description Usage Arguments.. ". Value. Warning. Details References See Also. Examples Run this code # one-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov .
iphone 7 drop test with cases
I have a dataset and would like to figure out which distribution fits my data best. I used the fitdistr() function to estimate the necessary parameters to describe the assumed distribution (i.e. Weibull, Cauchy, Normal). Using .
2.6 Kernel density estimation with ks. The density function in R presents certain limitations, such as the impossibility of evaluating the kde at arbitrary points, the unavailability of built-in transformations, and the lack of a multivariate extension. The ks package () delivers the ks::kde function, providing these and other functionalities. It will be the workhorse for carrying out .Performs a two-sided KS test for \(H_0: X \sim t_{\nu}\) with \(c\), scale \(s\), and degrees of freedom \(\nu\). If parameters are not specified, the MLE given the data will be used (see fitdistr ). For estimated parameters of the t-distribution the p-values are incorrect and should be adjusted. . See ks.test and the references therein .This function executes a bootstrap version of the univariate Kolmogorov-Smirnov test which provides correct coverage even when the distributions being compared are not entirely continuous. Ties are allowed with this test unlike the traditional Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Rdocumentation. powered by. Learn R Programming. Matching (version .
Performs two-sample nonparametric multivariate test of means based on the minimum spanning tree (MST) and Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic. It tests the null hypothesis that a set of features has the same mean in two conditions versus different means.
From my understanding strong deviatons in the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test show a poor goodness of fit. Is the problem likely with my beta-distribution, or do I need to transform my data in some way? I know there a couple outliers in the data (below) but there are a lot of data points (5915 NDVI observations), and quite mean centered.# Comparison of results obtained from dgof::ks.test # and KSgeneral::disc_ks_test, when F(x) follows the discrete # Uniform[1, 10] distribution as in Example 3.5 of # Dimitrova, Kaishev, Tan (2020) # When the sample size is larger than 100, the # function dgof::ks.test will be numerically # unstable x3 <- sample(1: 10, 25, replace = TRUE .
Para realizar la prueba de KS necesitamos instalar el paquete “ dgof ” usando la función install.packages() desde la consola R. install.packages("dgof") Paso 2: después de una instalación exitosa del paquete, . Visualización del Test de Kolmogorov-Smirnov en R.
An Anderson-Darling Test is a goodness of fit test that measures how well your data fit a specified distribution. This test is most commonly used to determine whether or not your data follow a normal distribution.. This type of test is useful for testing for normality, which is a common assumption used in many statistical tests including regression, ANOVA, t-tests, and .Performs the Lilliefors (Kolmogorov-Smirnov) test for the composite hypothesis of normality, see e.g. Thode (2002, Sec. 5.1.1). Rdocumentation. powered by. Learn R Programming. nortest (version 1.0-4) Description Usage Arguments. Value. Details References See Also, , , .
I am going to use the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to test normality of MYDATA in R. This is an example of what I do ks.test(MYDATA,"pnorm",mean(MYDATA),sd(MYDATA)) Here is the result R gives me: d.
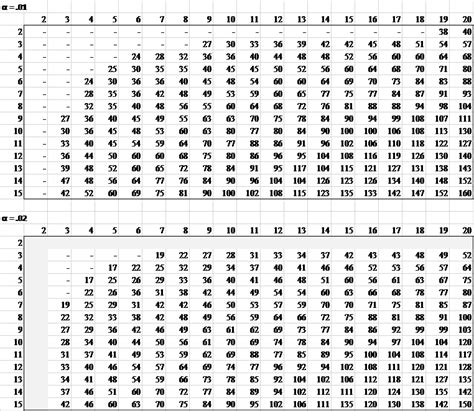
ks test critical value table
webManhunt.net gives you the ability to cruise over 6 million men since it is the biggest gay sex and gay video chat site for men seeking men in the world. Some of the most unique features to Manhunt.net include gay conversations, gay 1-to-1 video chat, free gay porn, and explicit gay content. Being a member of this gay community will help you .
ks test r package|kolmogorov smirnov test example